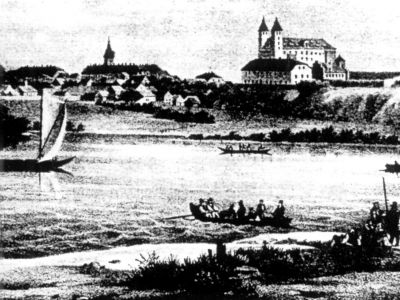Miasto i Gmina Gniew
Menu witryny
Treść strony
Gniew in the Republic
After returning to Poland, Gniew has become the seat of the governor, and the castle his residence. Actions of governors, development of the free navigation on the Vistula and recovery on land routes caused the gradual development of Gniew as the craft and trade centre of the Gdansk Pomerania. The reformation has also had a significant impact on the internal situation of Gniew.
In 1538 the municipal authorities and most of the townspeople went to Protestantism, and in 1570 the city received the religious privilege. In 1589, Zygmunt III Waza approved the Gniew Danzig Law, which is a set of internal laws of the city.
A long period of peace and development of the city has been interrupted by the wars with Sweden. In 1626, the enemy troops occupied Gniew. This led to the battle of Gniew, called the “battle of two Wazas”. However, the Swedish army on the castle has not been defeated.
Only next year the Polish army commanded by Stanislaw Koniecpolski pushed the Swedes out. Once again, the Swedish army appeared in Gniew in 1665. The storming of the city and the castle left behind extensive damage. In the period between the Swedish wars, prince Albrecht Stanislaw Radziwiłł – the governor of Gniew – has been positively distinguished. He often visited Gniew and took care of its development. He has particularly connected to the nearby Piaseczno, where his wife has been cured.
A successful period for the development of Gniew took place after 1667, when the county of Gniew was taken over by the hetman Jan Sobieski, the successive king of Poland. The new governor has significantly contributed to the reconstruction and development of the city after the devastating Swedish wars. The palace has been preserved until this day, which has been built by the king for his wife, Maria Kazimiera. The king has also rebuilt the church in Piaseczno.
The successors of Sobieski had to manage in difficult times. In 1703, during the Great Northern War, the Swedish army has entered Gniew for the third time. The city has been partially damaged, and the residents had to pay high contributions.
As a result of the I partition of Poland in 1772, Gniew along with Gdansk Pomerania were incorporated to Prussia, and it received the official name of “Mewe”. The influx and settlement of the German people started.
Polecamy
Dofinansowanie
Strona sfinansowana została ze środków Ministerstwa Administracji i Cyfryzacji, w ramach konkursu na budowę strony internetowej oraz dostosowanie jej do potrzeb osób niepełnosprawnych.
Kontakt

Urząd Miasta i Gminy Gniew
Plac Grunwaldzki 1, 83-140 Gniew
pon., wt., czw. 7.30-15.30
śr. 7.30-17.00
pt. 7.30-14.00
tel. 58 530 79 19;
fax 58 530 79 40
e-mail: sekretariat@gniew.pl
DANE DO FAKTURY
Gmina Gniew
NIP 593 10 05 516
REGON 191675296
Adres Elektronicznej Skrzynki Podawczej: /34gu04waml/skrytka
Adres do e-Doręczeń: AE:PL-20551-72681-DHGGB-31